
Selling restricted products online in the U.S. is becoming more complex due to evolving regulations. From stricter product safety rules to enhanced seller verification and data privacy requirements, compliance is now a top priority for ecommerce businesses. Failing to meet these standards can result in penalties, account suspensions, or legal issues. Here’s a quick breakdown of the five key regulatory trends you need to know:
- Marketplace Liability: Platforms like Amazon now enforce stricter seller verification under the INFORM Consumers Act. High-volume sellers must provide detailed information or risk suspension.
- Product Safety Rules: By July 8, 2026, importers must electronically file safety certificates for all regulated products. Non-compliance can lead to shipment delays.
- Data Privacy & Age Verification: Updated COPPA rules and state laws require robust age-gating and stricter controls for handling children’s data.
- Payment Security: New rules like PCI DSS v4.0 mandate stronger encryption and multi-factor authentication for payment systems.
- Automated Compliance Monitoring: Regulators and platforms now use AI to flag non-compliance, requiring sellers to maintain accurate and up-to-date information.
These changes demand immediate action to avoid disruptions. Sellers must prioritize accurate documentation, strong security measures, and responsive systems to stay compliant and maintain marketplace access.
5 Key Ecommerce Compliance Trends: Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
A Guide to Ecommerce Compliance in 2024
1. Increased Marketplace and Platform Liability
As of June 27, 2023, the INFORM Consumers Act has placed direct responsibility on marketplaces to ensure seller compliance. Platforms like Amazon, Walmart, and TikTok Shops are now required to collect, verify, and disclose specific information about high-volume third-party sellers. This step aims to reduce the risks associated with counterfeit, stolen, or dangerous products. These changes come with clear obligations for sellers, which are summarized below.
Operational changes for ecommerce sellers
If you’re a high-volume seller – defined as completing 200 or more individual sales and generating $5,000 or more in revenue within any 12-month period over the past two years – you’ll need to act fast. Within 10 days of receiving a request, you must provide marketplaces with the following:
- Banking details (account number or payee name)
- Contact information (your name or a government-issued ID for businesses)
- Business or taxpayer identification number
- A current email address and phone number
For sellers earning $20,000 or more in gross annual revenue, there’s an additional requirement: you must disclose your full name, physical address, and contact details on product listings or order confirmations. This information must also be certified annually within 10 days of the marketplace’s notification.
Risk mitigation strategies
Failing to comply with these requirements could lead to serious consequences. Marketplaces are now expected to suspend the accounts of sellers who fail to provide the necessary information, submit false details, or ignore consumer inquiries within a reasonable timeframe.
To avoid disruptions, set up internal systems to monitor your sales and revenue. This will help you stay on top of your compliance obligations as soon as you hit the high-volume threshold.
Keep your seller profile updated and respond promptly to any requests from the marketplace. If you qualify for partial disclosure exceptions – such as keeping your residential address private – ensure you certify these conditions accurately and remain responsive to customer inquiries. Any missteps could lead to immediate suspension of your account.
2. Stricter Product Safety, Labeling, and Documentation Requirements
Federal regulators are stepping up their game when it comes to product safety documentation. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has introduced a Final Rule requiring electronic filing (eFiling) of compliance certificates with U.S. Customs and Border Protection for all imported products regulated by the CPSC. This means that both Children’s Product Certificates (CPCs) and General Certificates of Conformity (GCCs) must be submitted digitally at the time of import.
Impact on Restricted Product Compliance
The eFiling mandate kicks in on July 8, 2026, for most products and on January 8, 2027, for items from foreign trade zones. By requiring digital submissions, the CPSC can evaluate health and safety risks before products hit U.S. shelves. This system flags shipments that fall short of safety standards while speeding up the process for sellers with compliant goods. With millions of low-value shipments flooding the U.S. daily, this data-driven method helps regulators focus their efforts where they’re needed most. It’s a proactive step to ensure stricter oversight of restricted products and paves the way for tougher enforcement measures.
Regulatory Enforcement Focus
CPSC is also holding online platforms accountable. In January 2025, the commission issued a Decision and Order against Amazon.com, Inc., covering over 400,000 hazardous products. These included faulty carbon monoxide detectors, hairdryers lacking electrocution protection, and children’s sleepwear that didn’t meet federal flammability standards. By classifying Amazon as a "distributor" under the Consumer Product Safety Act, the decision made the company legally responsible for recalling unsafe products sold through its Fulfilled by Amazon program.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
To stay ahead, businesses should act now. Start by updating your documentation systems. For children’s products, ensure you have valid CPCs based on third-party testing that complies with all relevant CPSC safety regulations. Automating compliance checks can help verify the accuracy of certificate data before shipping. Also, make sure your inventory is recall-free – selling recalled products is illegal, and regulators actively monitor marketplaces to catch violations.
3. Expanded Data Privacy, Identity Verification, and Age-Gating Rules
New U.S. regulations now emphasize stricter protections for children’s data and tighter controls on age verification for restricted products. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has updated the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) Rule, which will take effect in 2025. These updates significantly increase the compliance requirements for online platforms and retailers handling data from children under 13. Among the changes are more rigorous parental consent rules, especially for targeted advertising and sharing children’s data with third parties. At the same time, states across the U.S. are introducing laws requiring platforms to verify users’ ages before granting access to specific products or content. For ecommerce businesses, these changes mean immediate adjustments are necessary to stay compliant.
Operational Changes for Ecommerce Sellers
To meet these new requirements, basic methods like checkboxes or birthdate fields are no longer sufficient. Instead, implement multi-layered age verification systems. These can include document scanning, biometrics, and device-based checks to comply with both federal and local regulations.
Regulatory Enforcement Focus
Regulators are actively enforcing these new rules, with severe penalties for non-compliance. For example, in New York, first-time violations involving alcohol sales can result in fines of up to $10,000, while repeat offenses can exceed $20,000. The FTC imposes even steeper penalties under COPPA, with civil fines reaching $50,120 per violation. California’s Digital Age Assurance Act, effective January 1, 2027, will require operating systems to prompt users to provide their birth date or age when creating accounts. Additionally, the FTC is investigating AI chatbots for COPPA compliance, and California’s SB 243 mandates specific disclosures and safeguards for minors interacting with AI-powered tools.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
To navigate these changes, businesses should strengthen their data protection and age verification processes. Key steps include updating privacy policies, revising data retention schedules, and automating customer reverification for recurring transactions. Explicit consent should also be obtained for ID scans or biometric data collection. Furthermore, review advertising practices to ensure they align with the new restrictions – avoid conditioning website access on parental consent for targeted ads. These measures can help minimize risks while ensuring compliance with evolving regulations.
sbb-itb-e2944f4
4. Stronger Payment Security and Transaction Monitoring Standards
Payment security regulations have tightened significantly, building on stricter marketplace liability standards. For instance, compliance with PCI DSS v4.0 will become mandatory by March 31, 2025, introducing requirements like passwords with at least 12 characters and quarterly vulnerability scans. Additionally, the INFORM Consumers Act now requires online marketplaces to verify high-volume sellers’ bank account details, tax IDs, and contact information within 10 days.
Impact on Restricted Product Compliance
These enhanced security measures aim to curb unauthorized sales of restricted products. By integrating verified seller information with advanced transaction monitoring tools, online marketplaces can more effectively detect suspicious activities. This not only reduces the risk of financial fraud but also helps prevent data breaches.
Operational Changes for Ecommerce Sellers
Ecommerce sellers face new operational demands. Beyond basic verification, they must adopt stronger security measures, such as conducting written risk assessments, implementing encryption, and using multi-factor authentication. For example, the FTC’s Safeguards Rule (16 CFR Part 314), effective December 12, 2025, requires financial institutions – including ecommerce platforms and payment processors – to encrypt customer financial data and use multi-factor authentication for accessing systems containing sensitive information.
Regulatory Enforcement Focus
Regulatory bodies like the FTC and state attorneys general are now intensifying their enforcement of these standards. The FTC’s Safeguards Rule emphasizes the need for rigorous data security measures in all payment-related activities.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
To stay compliant, sellers should regularly conduct written risk assessments to identify potential threats to customer data. Strong security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, are critical to prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, specialized fraud mitigation services became available in 2025, offering support for managing and recovering losses from fraudulent transactions. Sellers must also act swiftly to address any discrepancies flagged by marketplaces to avoid disruptions in their sales operations.
5. Data-Driven Risk Management for Restricted Products
Regulators and online marketplaces are increasingly turning to advanced analytics and automation to ensure compliance for restricted products. This shift allows for faster, more efficient monitoring of ecommerce compliance in real time.
Impact on Restricted Product Compliance
The INFORM Consumers Act has introduced automated seller verification processes, requiring sellers to provide bank details, tax IDs, and government-issued IDs. These measures aim to prevent data falsification and swiftly identify non-compliant listings. At the same time, the FTC has begun using AI-powered systems to detect deceptive practices and unauthorized sales of restricted items. These tools enable regulators to catch violations before they impact consumers.
Operational Changes for Ecommerce Sellers
For sellers, staying compliant means keeping product and identity information accurate and up to date across all marketplace systems. This includes ensuring product safety documentation is complete and items are categorized correctly to avoid triggering automated risk alerts.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Marketplace dashboards are essential tools for sellers looking to manage compliance effectively. Platforms like Walmart’s Seller Center provide real-time data on sales, orders, and product performance. By using these insights alongside proactive listing management, sellers can stay ahead of potential compliance issues. Regularly reviewing dashboard data allows sellers to address problems early – before automated systems flag them.
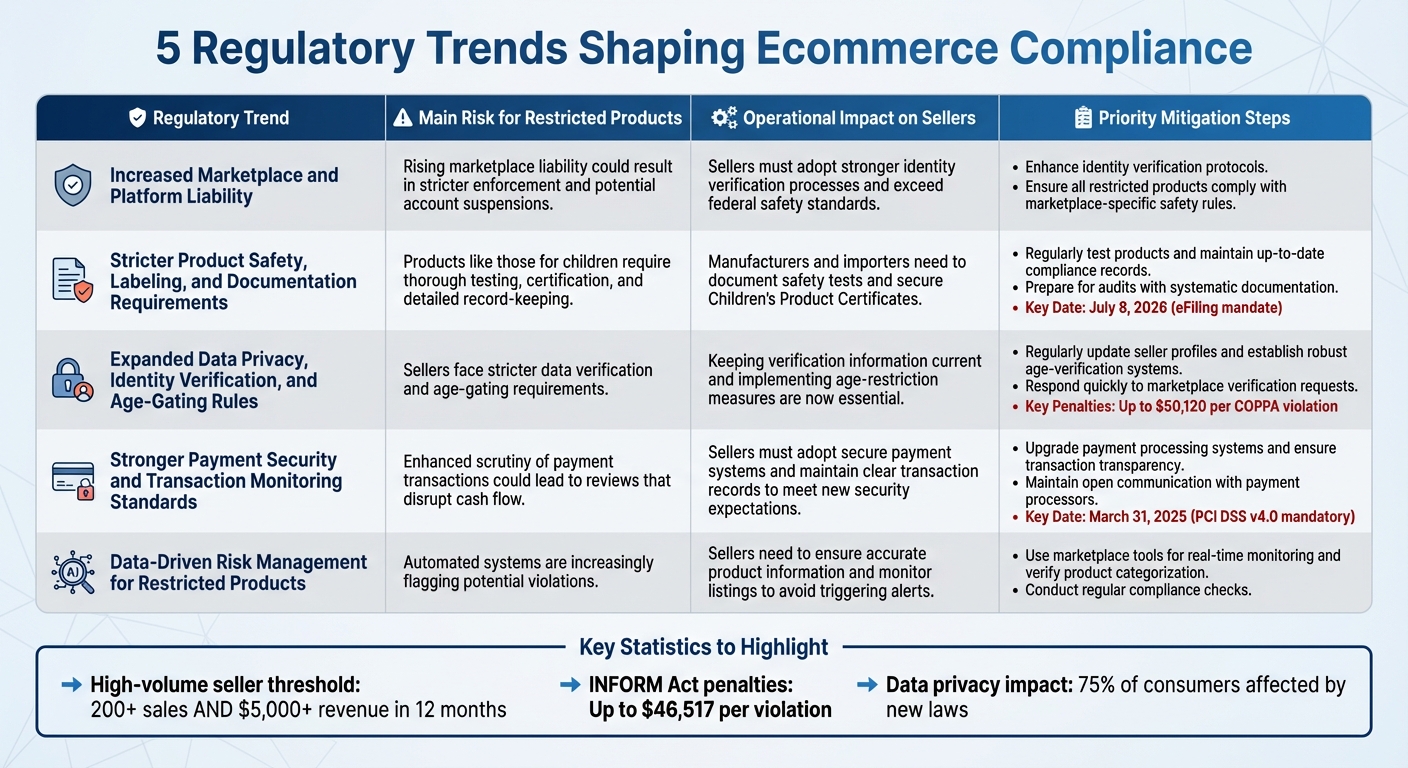
Comparison Table
The table below outlines how various regulatory trends affect sellers of restricted products and suggests key steps to address these challenges.
| Regulatory Trend | Main Risk for Restricted Products | Operational Impact on Sellers | Priority Mitigation Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Marketplace and Platform Liability | Rising marketplace liability could result in stricter enforcement and potential account suspensions | Sellers must adopt stronger identity verification processes and exceed federal safety standards | Enhance identity verification protocols and ensure all restricted products comply with marketplace-specific safety rules |
| Stricter Product Safety, Labeling, and Documentation Requirements | Products like those for children require thorough testing, certification, and detailed record-keeping | Manufacturers and importers need to document safety tests and secure Children’s Product Certificates | Regularly test products, maintain up-to-date compliance records, and prepare for audits with systematic documentation |
| Expanded Data Privacy, Identity Verification, and Age‑Gating Rules | Sellers face stricter data verification and age-gating requirements | Keeping verification information current and implementing age-restriction measures are now essential | Regularly update seller profiles, establish robust age-verification systems, and respond quickly to marketplace verification requests |
| Stronger Payment Security and Transaction Monitoring Standards | Enhanced scrutiny of payment transactions could lead to reviews that disrupt cash flow | Sellers must adopt secure payment systems and maintain clear transaction records to meet new security expectations | Upgrade payment processing systems, ensure transaction transparency, and maintain open communication with payment processors |
| Data‑Driven Risk Management for Restricted Products | Automated systems are increasingly flagging potential violations | Sellers need to ensure accurate product information and monitor listings to avoid triggering alerts | Use marketplace tools for real-time monitoring, verify product categorization, and conduct regular compliance checks |
This table underscores the importance of robust identity verification and detailed documentation as cornerstones of a solid compliance strategy for sellers of restricted products.
Conclusion
For marketplace sellers, compliance isn’t optional – it’s essential. With penalties as steep as $46,517 per violation under the INFORM Consumers Act and the looming threat of account suspensions, the risks of non-compliance far outweigh the costs of proactive risk management. As BigCommerce aptly puts it:
Reaching and maintaining full compliance with all ecommerce-related regulations isn’t optional. It’s a mandatory business need, no matter if you’re running a global enterprise or a small business.
The regulatory landscape is shifting quickly. For instance, the CPSC’s eFiling initiative begins on July 8, 2026, and data privacy laws now impact 75% of consumers. These changes demand that sellers implement forward-thinking compliance systems. Failing to do so can lead to shipment delays, port issues, and even marketplace account suspensions – disruptions that can severely impact cash flow and customer confidence.
In this dynamic environment, successful sellers treat compliance as a strategic advantage. By verifying seller data, keeping thorough documentation, and preparing for standards like PCI DSS 4.0, they not only meet regulations but also build trust with both marketplaces and consumers. Practices such as monitoring transaction volumes and maintaining meticulous records are no longer optional – they’re critical for sustained growth.
For brands navigating these challenges, Emplicit offers tailored solutions to ensure documentation accuracy and real-time monitoring. Their comprehensive approach allows brands to focus on scaling their business while staying ahead of regulatory demands.
Taking action now is key to safeguarding marketplace access and avoiding hefty penalties. Sellers who prioritize robust compliance frameworks today will position themselves to maintain access and earn enduring consumer trust.
FAQs
What do ecommerce sellers need to do to comply with the INFORM Consumers Act?
Ecommerce sellers should check if they fall under the category of high-volume third-party sellers. This applies to those who have completed more than 200 transactions and earned over $5,000 in gross revenue within a 12-month period. Meeting this threshold means sellers are required to provide the marketplace with a government-issued ID, tax ID, bank account details, and accurate contact information.
On top of that, sellers must certify this information every year, ensure it’s safeguarded with proper security protocols, and display their name, physical address, and contact details on product listings for buyers. Following these rules is crucial to avoid penalties and build trust with both the marketplace and customers.
How can ecommerce businesses comply with new privacy and age verification regulations?
To keep up with changing data privacy laws, businesses need to start by pinpointing where their customers are located and understanding the specific regulations that apply in those areas. For example, upcoming regulations like the Kentucky Consumer Data Privacy Act and changes to FTC rules under COPPA will introduce tighter rules on how businesses collect, share, and obtain consent for user data starting in 2026. A good first step is to perform a data inventory audit, categorize data based on its sensitivity, and set up consent workflows that comply with these new rules.
When it comes to age verification, states such as California and Texas are rolling out stricter requirements. These include verifying users’ ages through government-issued IDs or obtaining parental consent. Businesses should consider using trusted third-party age-verification tools, ensure the secure storage of verification data, and revise their privacy policies to outline these processes. Working with a compliance partner like Emplicit can make this easier. They offer tailored solutions for privacy updates, age-verification systems, and ongoing monitoring of regulations – helping your business stay compliant without compromising the customer experience.
How can sellers improve payment security and stay compliant with e-commerce regulations?
To strengthen payment security and align with e-commerce compliance requirements, sellers should implement the latest Payment Security Standards v4.0 (PCI DSS). Key measures include encrypting cardholder data, utilizing tokenization to protect sensitive information, and enabling multi-factor authentication for all transactions. Conducting regular security assessments and vulnerability scans is equally important to maintain compliance and address potential risks.
As AI-driven fraud becomes a growing concern, sellers must adopt real-time fraud detection tools to identify unusual activity, enhance identity verification procedures, and educate staff on recognizing phishing attempts. These measures not only protect transactions but also help prevent fraud and avoid expensive regulatory fines.
